THE INFORMATION IN THIS ARTICLE APPLIES TO:
- EFT Server (All Versions)
- Secure FTP Server (All Versions)
- CuteFTP (All Versions)
QUESTION
Can I use a Windows Command Prompt to send FTP Commands to the Server?
ANSWER
Using CuteFTP, you can communicate with an FTP site on the lowest possible level. You can define an FTP site in the Site Manager, then simply double-click it to connect and log in. Using CuteFTP's Custom Commands dialog box, you can define command sequences for common tasks, and place shortcuts for the commands on the toolbar for reuse. CuteFTP makes FTP simple; however, if you prefer to use a Windows Command Prompt, the procedure and table below will help you with some of the more common FTP tasks.
To use FTP commands at Windows command prompt
-
Open a command prompt and navigate to the folder containing the files that you want to transfer, then press ENTER. For example, type:
cd "C:\Documents and Settings\marsha\My Documents\CaseStudies" (You need the quotes if you have spaces in your path.)
-
At the C:\> prompt, type FTP. The C:\> prompt changes to ftp>.
-
At the ftp> prompt, type open followed by the name of the remote FTP site, then press ENTER. For example, type:
open myftpsite.com
-
When prompted, type the username and password provided to you by the administrator of the FTP site, then press ENTER.
|
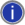
|
If you get a 10061 error, it is likely the site is refusing to accept your connection because of security privileges or because it is not an FTP server. For a list of FTP error codes, refer to Knowledge Base article 10142, FTP Status and Error Codes.
|
-
Type cd then the path to the remote server's directory in which you have permission to transfer files via FTP. For example, type:
cd M:\InetPub\EFTRoot\MySite\Usr\jbug
You are now ready to transfer files between your local directory and the remote directory using FTP commands such as put and get.
DOS FTP commands are slightly different than regular FTP commands. The table below lists some of the more common FTP commands as you would enter them at a Windows Command prompt. (Certain DOS commands also work in UNIX, but UNIX directories use a forward slash ( / ); DOS directories use a back slash ( \ ).)
|

|
If you want to issue a command that is understood by a remote FTP server, but not by DOS, use the literal command in front of the FTP command. This command allows you to pass any request to the remote server without its being a valid DOS command.
|
|
Change user password on a site
|
Literal SITE PSWD oldpassword newpassword
|
"Literal" sends a command line to the remote FTP connection and executes the SITE PSWD command.
|
|
Connect to the specified FTP host
on the specified port
|
open [host] [port]
|
For example, type:
open myftpsite.com 21
|
|
Navigate to a different directory
on remote machine
|
cd [directory]
|
For example, type:
cd M:\InetPub\EFTRoot\MySite\Usr\jbug
|
|
Change to parent directory
|
cdup
|
Same as cd ..\
|
|
Changes directory on local
machine
|
lcd [path]
|
For example, type lcd c:\temp.
|
|
Displays a list of files and
folders in the current remote directory
|
dir [path]
ls [directory] [localfile]
|
For example, type:
dir M:\InetPub\EFTRoot\MySite\Usr\jbug
or
ls M:\InetPub\EFTRoot\MySite\Usr\jbug C:\temp\contents.txt
|
|
Creates a directory on the remote
file system
|
mkdir [name]
|
For example, to create a folder into which you will upload your graphics files, type:
mkdir images
|
|
Copies a file from the local to
the remote computer
|
put [filename.ext]
|
To upload the file with a different name, use
put oldfilename.ext newfilename.ext
|
|
Copies multiple files from the
local to the remote computer
|
mput [files]
|
Puts multiple files; *.* puts all files; *.txt puts all .txt files, my_*.* puts all files that start with my_ with any extension.
|
|
Copies a file from the remote to
the local computer
|
get [filename.ext]
|
For example, type:
get dog.jpg
|
|
Copies multiple files from the
remote to the local computer
|
mget [files]
|
Gets multiple files; *.* gets all files; *.txt gets all .txt files, my_*.* gets all files that start with my_ with any extension.
|
|
Deletes a file
|
delete [filename.ext]
|
For example, type:
delete dog.jpg
|
|
Renames a file
|
rename [filename] [filename]
|
For example, to rename a picture of your dog, Pooh Bear, type:
rename dog.jpg PoohBear.jpg
|
|
Removes a directory on the remote
computer
|
rmdir [name]
|
For example, type:
rmdir olddogpics
|
|
List current working directory
|
pwd
|
Use when you forget which directory you are in or if you want to copy the path
|
|
Close connection
|
bye (or quit)
|
Disconnect from remove FTP server
|
|
List of available commands or
help for a specific command
|
help
help [command]
? [command]
|
help by itself lists available FTP commands; help [command] or ? [command] provides help for the specific command
|
|
Change transfer mode to ASCII
|
ascii
|
Used for HTML and text files
|
|
Change transfer mode to binary
|
binary
|
Used for graphics, compressed files, audio clips, etc.
|
|
Displays current transfer mode
(ASCII or binary)
|
status
|
Query the status of files, transfers in process, and other system information. The STAT command implemented on some FTP servers could allow a remote attacker to obtain sensitive information; therefore, it is disabled on some servers.
|
|
Enable/disable prompts
|
prompt
|
Use this command if you do not want to be prompted for each file transfer when transferring multiple files.
|